According to global health data, most women experience over 450 menstrual cycles in their lifetime. Yet many still feel unsure about what actually happens during each phase. The phases of menstrual cycle explain why energy, mood, and body responses change throughout the month. Understanding the menstrual cycle phases in order helps women manage health, fertility, and lifestyle decisions better. This guide explains the four menstrual phases clearly, in the correct order of menstrual cycle, with practical and relatable insights.
What Is the Menstrual Cycle and Why It Matters
The menstrual cycle is a monthly biological process that prepares the female body for pregnancy. It begins on the first day of menstrual bleeding and ends just before the next period starts. The phases of menstrual cycle are controlled by hormones released from the brain and ovaries. These hormones guide ovulation, uterine lining changes, and menstruation.
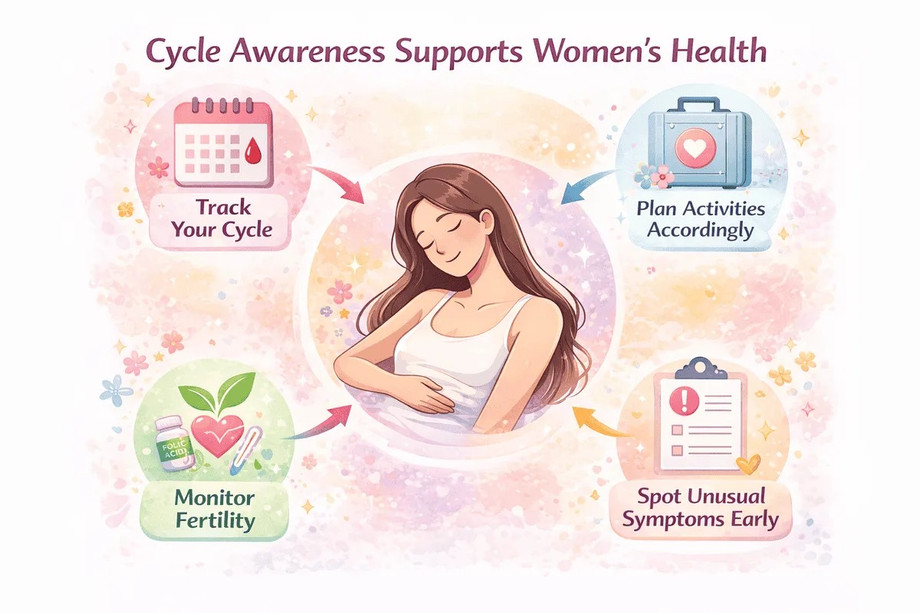
Knowing the menstrual cycle phases in order matters because it helps women understand what is normal for their body. Cycle awareness supports better planning for work, exercise, travel, and emotional wellbeing. It also helps identify irregularities such as delayed periods or severe symptoms early. Many women use cycle knowledge to track fertility and hormonal balance naturally.
Each cycle follows the same sequence but length and symptoms can vary. Stress, nutrition, sleep, and lifestyle influence how each phase feels. Learning about the cycle builds confidence and reduces confusion around periods. For a detailed overview of how the cycle works, explore this complete guide on menstrual cycle basics available on Menstrual Cycle.
You can also learn more from the women health education category that covers cycle related topics in depth.
Phase 1 Menstrual Phase Explained In Detail
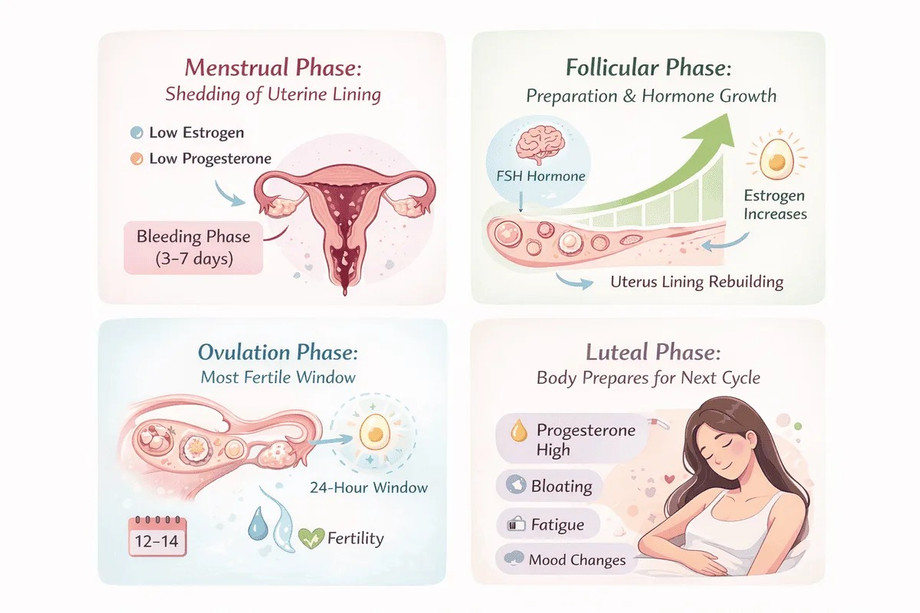
The menstrual phase is the first stage in the order of menstrual cycle. It begins when the uterus sheds the lining built during the previous cycle. This shedding appears as menstrual bleeding. The phase usually lasts between three to seven days depending on individual health and cycle pattern.
During this phase estrogen and progesterone levels drop significantly. This hormone drop signals the uterus to release the old lining. Blood, tissue, and mucus exit the body through the vagina. Many women experience cramps, back pain, fatigue, or headaches due to uterine contractions. These contractions help push the lining out.
Emotionally this phase may feel slower or more inward focused. Energy levels are often lower. The body is in a reset mode. Rest, hydration, and gentle movement support comfort during this phase. Light stretching or walking may help reduce stiffness. For natural comfort practices during periods, refer to this period care and hygiene guide on the menstrual cycle.
This phase prepares the body for the next set of hormonal changes. Even though it marks the start of the cycle, it overlaps with the early follicular phase internally. Understanding this helps women view menstruation as a functional and healthy process, not just bleeding.
Hormonal Events During Menstruation
Hormonal activity during menstruation is defined by low estrogen and progesterone levels. These low levels cause the uterine lining to break down and shed. Prostaglandins increase to stimulate uterine contractions. Higher prostaglandin levels often result in stronger cramps. Hormones begin to rise slowly toward the end of this phase. This rise signals the body to prepare a new egg for the upcoming cycle.
Common Signs And Experiences In This Phase
Common signs include menstrual bleeding, cramps, bloating, fatigue, and mood sensitivity. Appetite changes and sleep disturbances are also reported by many women. Symptoms differ each cycle depending on stress and health. Tracking symptoms monthly helps identify patterns. This awareness supports better planning and self care.
Phase 2 Follicular Phase Uncovered
The follicular phase begins on the first day of menstruation and continues until ovulation. It overlaps with the menstrual phase initially. This phase focuses on preparation. The brain releases follicle stimulating hormone, which signals the ovaries to develop follicles. Each follicle contains an immature egg.
As follicles grow, estrogen levels increase steadily. Rising estrogen rebuilds the uterine lining. This lining becomes thicker and richer to support possible pregnancy later. Women often feel more motivated and mentally clear during this phase. Skin texture and digestion may also improve.
The follicular phase length varies across cycles. It is the most flexible phase of the four menstrual phases. Healthy nutrition, proper sleep, and reduced stress support hormone balance here. Many women find this phase ideal for starting new routines or tasks.
To understand hormonal balance better during this stage, visit the hormonal health guide on Menstrual Cycle.
You can also explore insights from the menstrual health awareness to learn how lifestyle supports cycle regularity.
Hormonal And Physical Processes In Follicular Phase
Estrogen rises gradually throughout this phase. This hormone improves blood flow to the uterus and supports lining growth. Follicle stimulating hormone encourages egg development. The dominant follicle releases more estrogen as it matures. This hormonal activity prepares the body for ovulation. Physical energy often increases alongside hormonal stability.
How Follicular Phase Sets The Stage For Ovulation
As estrogen peaks, it signals the brain to release luteinising hormone. This surge triggers ovulation. The follicular phase ends once the egg is released. The uterus is now ready to receive a fertilised egg. Understanding this transition helps women track fertility accurately. This knowledge is especially useful for cycle planning.
Phase 3 Ovulation Phase In The Menstrual Cycle
Ovulation is the shortest yet most significant phase in the menstrual cycle phases in order. It usually occurs around the middle of the cycle. A surge of luteinising hormone releases a mature egg from the ovary. The egg travels into the fallopian tube where fertilisation can occur.
The egg survives for about twenty four hours. This is the most fertile window of the cycle. Many women notice physical signs like clear stretchy discharge, slight pelvic discomfort, or increased confidence. These signs help identify ovulation without medical tools.
Ovulation represents peak reproductive readiness. Hormonal balance is high during this phase. Energy, communication skills, and social comfort often improve. For those tracking fertility, ovulation awareness is essential.
Learn more about recognising ovulation naturally in this ovulation tracking guide on Menstrual Cycle.
You can also explore fertility related insights in the cycle tracking category for deeper understanding.
What Triggers Ovulation In The Cycle
Ovulation is triggered by a sharp rise in luteinising hormone. This rise occurs after estrogen reaches a specific level. The hormone surge causes the follicle to rupture. The egg is released into the fallopian tube. Timing this surge helps identify fertile days accurately.
Signs Of Ovulation To Watch For
Common ovulation signs include slippery cervical mucus and mild lower abdominal sensation. Some women notice breast tenderness or heightened senses. Basal body temperature rises slightly after ovulation. Observing these signs consistently improves cycle awareness. This awareness supports informed reproductive decisions.
Phase 4 Luteal Phase Explained Clearly
The luteal phase begins immediately after ovulation and lasts until menstruation. The empty follicle transforms into the corpus luteum. This structure releases progesterone. Progesterone stabilises the uterine lining and prepares it for implantation.
If pregnancy occurs, progesterone remains high. If pregnancy does not occur, progesterone drops gradually. This hormone decline causes the uterine lining to shed. Premenstrual symptoms often appear during this phase. These include bloating, mood changes, fatigue, or cravings.
The luteal phase length is usually consistent across cycles. Tracking this phase helps identify hormonal health. Lifestyle support during this time improves comfort. Balanced meals and stress reduction are helpful.
For managing premenstrual symptoms naturally, explore this premenstrual care guide on Menstrual Cycle.
You can also read more from the women wellness category focused on cycle aligned lifestyle tips.
Hormonal Activity During Luteal Phase
Progesterone dominates this phase. It slows digestion and increases body temperature slightly. Estrogen remains present but lower. Hormonal shifts influence mood and sleep patterns. Toward the end of the phase hormones decline. This decline signals menstruation.
Symptoms And Body Changes After Ovulation
Common symptoms include fatigue, breast tenderness, and emotional sensitivity. Some women experience bloating or headaches. These changes are linked to progesterone and estrogen shifts. Symptoms vary in intensity each cycle. Awareness helps women prepare mentally and physically.
Tracking And Understanding Your Cycle For Better Health
Tracking the phases of menstrual cycle improves long term health awareness. It helps identify irregular patterns early. Cycle tracking supports fertility planning and symptom management. Many women use apps, journals, or physical signs to track changes. Regular tracking builds confidence and clarity.
For simple and effective tracking methods, refer to this menstrual cycle tracking resource on Menstrual Cycle.
You can also browse the cycle education category for tools and guides.
Conclusion
Understanding the four menstrual phases gives clarity to monthly body changes. Knowing the order of menstrual cycle helps women manage health and lifestyle choices better. Each phase serves a purpose in reproductive wellbeing. Awareness reduces confusion and builds confidence. To explore more trusted menstrual health resources, visit the Menstrual Cycle and start learning more today.
FAQs
What Are The Four Phases Of Menstrual Cycle?
The four phases of menstrual cycle are menstrual, follicular, ovulation, and luteal. Each phase is controlled by specific hormones. These phases repeat every month in the same order. They prepare the body for possible pregnancy. Understanding them supports reproductive health awareness.
What Happens In The Luteal Phase Of The Menstrual Cycle?
The luteal phase starts after ovulation. Progesterone rises to support the uterine lining. If pregnancy does not occur hormone levels fall. This fall triggers menstruation. Many women experience premenstrual symptoms during this phase.
How Long Is Each Phase Of Menstrual Cycle?
The menstrual phase lasts three to seven days for most women. The follicular phase length varies. Ovulation lasts about one day. The luteal phase usually lasts around fourteen days. Total cycle length differs individually.
What Is The Order Of Menstrual Cycle Phases?
The cycle begins with menstruation. It then moves into the follicular phase. Ovulation follows next. The cycle ends with the luteal phase. After this menstruation starts again.
Why Tracking Menstrual Cycle Matters?
Tracking helps understand fertility windows and symptoms. It supports early detection of irregular cycles. Tracking improves lifestyle planning. It also builds body awareness. Consistency improves accuracy.
Can Menstrual Phase Vary In Length?
Yes menstrual length varies among women. Stress and health affect bleeding days. Some cycles are lighter or heavier. Variation can still be normal. Tracking helps identify patterns.
How To Improve Menstrual Health Naturally?
Balanced nutrition supports hormone health. Regular physical activity reduces discomfort. Stress management improves cycle balance. Adequate sleep supports recovery. Consistent tracking builds awareness.
Article source :- https://menstrualcycle.in/phases-of-menstrual-cycle/